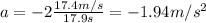Answer:
- 1.94 m/s^2
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
We can solve this problem using the equation of the velocity in terms of the time:
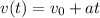
The velocity when the the rock returns to his hand must be the same but with opposite sign than the initial velocity, that is:
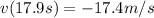
Therefore:
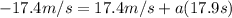
Solving for a: