Answer and Explanation:
Prokaryotic Translation :
Initiation :
- First amino acid participating is f-methionine.
- Requires three initiation components are
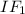 ,
,
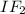 and
and
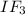
- Initiation complex framed at Shine-Dalgarno succession of mRNA.
- There is no concept of Kojak rule in prokaryotic.
Protein synthesis :
- Faster process. Adds 20 amino acids per sec.
Termination :After translation, the formyl group of first formylated methionine is removed. Methionine is retained in the polypeptide chain
Eukaryotic Translation :
Initiation :
- First amino acid taking part in translation if methionine.
- Requires a set of eleven initiation factors, named as eIFn.
- Initiation complex formed at 5’ end of mRNA.
- Kojak rule followed
Protein synthesis :
- Slow process. Adds 1 amino acid per second.
- mRNA is mono-cistronic.
- Occurs on 80S ribosome.
Termination :
Initiating methionine codon is removed from the polypeptide chain.