Answer:
60 people
Explanation:
The chance of getting a particular disease is
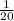
To calculate how much the chance is increased by smoking, you have to calculate the 20% of
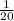 and then perform the sum of it and the original chance
and then perform the sum of it and the original chance
A 20% as a fractional number is
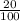
Therefore the 20% of
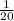 is:
is:
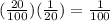
So, the chance of getting a particular disease sometime during the lifetime for a smoker is:
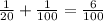
This means that every 100 smokers, 6 of them would get the disease.
You have to multiply the risk by the group of smokers to calculate how many people you would expect to get the disease:
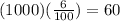
In conclusion, 60 people out of a group of 1000 people would get the disease.