Answer:
The convective coefficient is 37.3 W/m²K.
Step-by-step explanation:
Use Newton’s law of cooling to determine the heat transfer coefficient. Assume there is no heat transfer from the ends of electric resistor. Heat is transferred from the resistor curved surface.
Step1
Given:
Diameter of the resistor is 2 cm.
Length of the resistor is 16 cm.
Current is 5 amp.
Voltage is 6 volts.
Resistor temperature is 100°C.
Room air temperature is 20°C.
Step2
Electric power from the resistor is transferred to heat and this heat is transferred to the environment by means of convection.
Power of resistor is calculated as follows:
P=VI
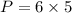
P= 30 watts.
Step3
Newton’s law of cooling is expressed as follows:
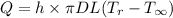
Here, h is the convection heat coefficient and
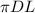 is the exposed surface area of the resistor.
is the exposed surface area of the resistor.
Substitute the values as follows:
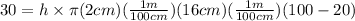
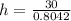
h = 37.3 W/m²K.
Thus, the convective coefficient is 37.3 W/m²K.