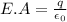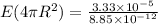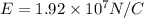Answer:
Part a)
Gaussian Surface must be spherical
Part b)
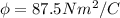
Part c)
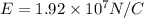
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a)
We can build a spherical Gaussian surface around a point charge
Because the flux of electric field around the spherical Gaussian surface will be uniform throughout the surface.
Part b)
Area of the cushion is given as
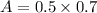
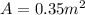
now electric field has two components
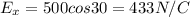
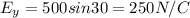
now we know that flux due to horizontal component of field is zero
while flux due to vertical component is given as
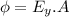
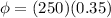
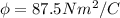
Part c)
Electric flux due to a spherical surface is given as