Answer: The mass of decane produced is

Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
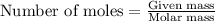 ......(1)
......(1)
Mass of hydrogen gas = 2.45 g
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1:, we get:
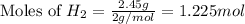
The chemical equation for the hydrogenation of decene follows:
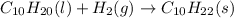
As, decene is present in excess. So, it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, hydrogen gas is a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of products.
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of hydrogen gas produces 1 mole of decane.
So, 1.225 moles of hydrogen gas will produce =
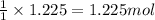 of decane
of decane
Now, calculating the mass of decane by using equation 1, we get:
Moles of decane = 1.225 mol
Molar mass of decane = 142.30 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
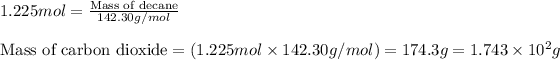
Hence, the mass of decane produced is
