Step-by-step explanation:
Here it is given that carbon is sample 2 = 25.9 g
- For sample 1, mass carbon = 1.47 g
No. of moles of carbon will be calculated as follows.
No. of moles of carbon =
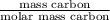
=
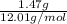
= 0.1224 mol
It is also given that mass of hydrogen = 0.123 g
Hence, calculate number of moles of hydrogen as follows.
No. of moles of hydrogen =
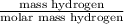
=
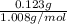
= 0.122 mol
Therefore,
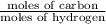
=
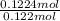
= 1.003
- For sample 2, mass of hydrogen = 2.17 g
Therefore, calculate the number of moles of hydrogen as follows.
No. of moles of hydrogen =
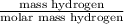
=
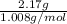
= 2.1528 mol
Hence, calculate the moles of carbon as follows.
Moles of carbon =
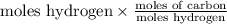
=
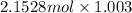
= 2.16 mol
Mass of carbon = moles carbon × molar mass carbon
= (2.16 mol) × (12.01 g/mol)
= 25.9 g
Thus, we can conclude that 25.9 g of carbon is expected in the sample.