Answer:
-0.93 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
The freezing-point depression is given by:
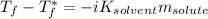
Whereas
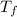 is the freezing temperature of the solution,
is the freezing temperature of the solution,
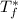 is the freezing temperature of the pure solvent (0 °C since it is water),
is the freezing temperature of the pure solvent (0 °C since it is water),
 the Van't Hoff factor (1 since the solute is covalent),
the Van't Hoff factor (1 since the solute is covalent),
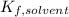 the solvent's freezing point depression point constant (in this case
the solvent's freezing point depression point constant (in this case
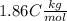 ) and
) and
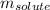 the molality of the glucose.
the molality of the glucose.
As long as the unknown is
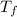 , solving for it:
, solving for it:
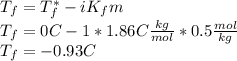
Best regards.