Step-by-step explanation:
An isotope is defined as the specie which contains same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
For example,
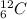 and
and
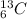 are isotopes.
are isotopes.
In a neutral carbon atom, there are 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
As it is known that in a neutral atom the number of protons equal to the number of electrons.
This means that in a neutral carbon atom there are also 6 electrons.
Whereas
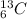 is an isotope of carbon atom whose atomic number is 6 and atomic mass is 13.
is an isotope of carbon atom whose atomic number is 6 and atomic mass is 13.
Hence, calculate the number of neutrons in
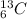 as follows.
as follows.
Atomic mass = no. of protons + no. of neutrons
13 = 6 + no. of neutrons
no. of neutrons = 13 - 6
= 7
Hence, in a
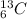 isotope of carbon atom there are 6 protons, 6 electrons and 7 neutrons.
isotope of carbon atom there are 6 protons, 6 electrons and 7 neutrons.
This shows that change in number of neutrons take place according to the definition of an isotope.