Answer:
The first solution has a final protein concentration of 0.0002 mg/ml.
To prepare the second solution, you have to take 56.25 ml of the stock solution 8 mg/ml and to add 43.75 ml of water.
Step-by-step explanation:
For this kind of dilution problems is very useful the following equation:
Cc x Vc = Cd x Vd
Where Cc and Vc are the concentration and volume of the more concentrated solution respectively, whereas Cd and Vc are the concentration and volume of the diluted concentration. If you know three of these four parameters, you can calculate the missing parameter.
For the first solution, you have the volume (0.200 ml) and concentration (1 mg/ml) of the more concentrated solution, and the volume of the diluted soluted is implied (final volume= 0.2 ml + 0.8 ml= 1 ml). Then,
Cc x Vc=Cd x Vd
0.200 ml x 1 mg/ml= Cd x 1 ml
⇒ Cd=
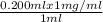 = 2 x 10⁻⁴ mg/ml= 0.0002 mg/ml
= 2 x 10⁻⁴ mg/ml= 0.0002 mg/ml
For the second solution, yo have the volume of the diluted solution (100 ml), the concentration of the diluted solution (4.5 mg/ml) and the concentration of the concentratesd solution (8 mg/ml). Then,
Cc x Vc= Cd x Vd
8 mg/ml x Vc= 100 ml x 4.5 mg/ml
⇒ Vc=
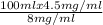 = 56.25 ml
= 56.25 ml
Thus, you have to take 56.25 ml of the more concentrated solution and to add the remaining volume of water to reach a final volume of 100 ml (100-56.25 ml= 43.75 ml)