Answer:
The mass of the air is 4.645 kg.
The work done or heat transfer is 277.25 kj.
Step-by-step explanation:
In isothermal process PV=constant. Take air as an ideal gas. For air gas constant is 287 j/kgK.
Given:
Initial pressure of the gas is 2 bar.
Initial volume of the gas is 2 m³.
Initial temperature is 300 K.
Final pressure is 1 bar.
Calculation:
Step1
Apply ideal gas equation for air as follows:
PV=mRT
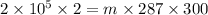
m = 4.645 kg.
Thus, the mass of the air is 4.645 kg.
Step2
For isothermal process work done is same as heat transfer.
Work done or the heat transfer is calculated as follows:
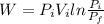
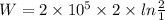
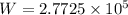 j
j
Or,
W=277.25 kj.
Thus, the work done or heat transfer is 277.25 kj.