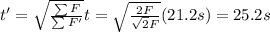Answer:
25.2 s
Step-by-step explanation:
In an uniformly accelerated motion starting from rest, the time taken for the motion is given by the equation
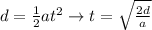
where t is the time, d is the distance covered, a is the acceleration.
We also know that the acceleration can be found by using Newton's second law:
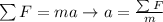
where
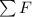 is the net force on the object and m its mass. Substituting into the previous equation,
is the net force on the object and m its mass. Substituting into the previous equation,
 (1)
(1)
So we see that the time taken for the motion is inversely proportional to the square root of the net force.
Let's consider now the space probe in the problem. Let's call F the magnitude of the force generated by each engine.
When the two forces are applied in the same direction, the net force on the space probe is
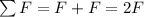
But when the two forces are applied perpendicularly, the net force is
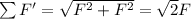
Using eq.(1) we can write:
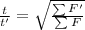
where t' is the new duration of the motion. Solving for t',