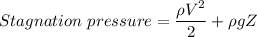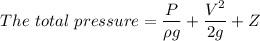Step-by-step explanation:
We know that Bernoulli equation is the energy conservation equation.This equation given as
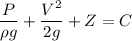
Where
P = Pressure
V= Velocity
Z= Elevation from reference
g= Acceleration due to gravity
ρ=Density
The above can be also written as
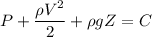
ρ g Z = Static pressure
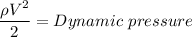
Stagnation pressure = Static pressure + Dynamic pressure