Answer:
False
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy required to break a bond is endothermic that is energy is absorbed to break a bond.
The energy is released in the formation of a bond that is energy is released when a bond is formed.
The formula to find the ∆H of the reaction is
∆H (reaction) = ∆H (bonds Broken) - ∆H (bonds formed)
For example
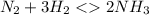
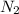 contains one N ≡ N triple bond (Bond breaking 946 KJ per mol)
contains one N ≡ N triple bond (Bond breaking 946 KJ per mol)
 contains a single H-H bond (bond breaking 436KJ per mol)
contains a single H-H bond (bond breaking 436KJ per mol)
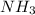 contains 3 N-H single bonds (389 KJ per mol)
contains 3 N-H single bonds (389 KJ per mol)
So,
∆H (bonds broken) = 946 + (3 × 436) = 2254 KJ
∆H (Bonds formed ) = (2 × 3 × 389) = 2334 KJ
So,
∆H (reaction) = 2254 KJ - 2334 KJ = - 80 KJ
The reaction is Exothermic
In this example we see energy required to break the bond is lesser than energy released in forming the bond.
So we can conclude if the amount of energy required to break bonds in the reactants is more than the amount of energy released in forming bonds in the products, then the reaction will have a positive change in enthalpy and ∆H is positive (+∆H) .