Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass of CS₂ = 0.15g
Volume of O₂ = 285mL
Condition of reaction = at standard temperature and pressure.
Solution:
Balanced reaction equation is shown below:
CS₂ + 3O₂ → CO₂ + 2SO₂
For gases at standard temperature and pressure(STP);
number of moles =
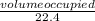
To find the final mixture of the gases at STP, we must identify the limiting reactant here first. The limiting reactant determines the extent of the reaction since it is the one used up.
Number of moles of CS₂ =
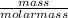
molar mass of CS₂ = 12 + (2 x 32) = 76g/mol
Number of moles of CS₂ =
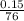 = 0.00197mole
= 0.00197mole
Number of moles of O₂ =
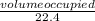
converting mL to dm³;
1000mL = 1dm³
285mL = 0.285dm³
Number of moles of O₂ =
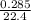 = 0.01272mole
= 0.01272mole
From the reaction equation:
1 mole of CS₂ reacted with 3 moles of O₂;
0.00197 mole of CS₂ will require 3 x 0.00197; 0.00591mole to react with;
We see that we have more than enough O₂. CS₂ is the limiting reagent.
Number of moles of excess O₂ = 0.01272 - 0.00591 = 0.00681moles
Now, we use the information of the limiting reagent to determine the product,
1 mole of CS₂ will produce 1 mole of CO₂;
0.00197 mole of CS₂ will produce 0.00197 mole of CO₂
1 mole of CS₂ will produce 2 mole of SO₂
0.00197mole of CS₂ will produce 2 x 0.00197; 0.00394mole of SO₂
The moles of the final mixture will = number of moles of excess O₂ + number of moles of CO₂ + number of moles of SO₂ = 0.00681+0.00197+0.00394
= 0.01272moles
Volume of the final mixture = number of moles x 22.4 = 0.01272 x 22.4
Volume of final mixture = 0.2849dm³ or 284.9mL