Answer:
Change
Step-by-step explanation:
The law of conservation of momentum states that, for a system of interacting objects that do not experience a net external force, the total momentum of the system is conserved.
This law can be demonstrated using Newton's second law:
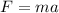
where
F is the net force acting on the system of objects
m is the total mass of the system
a is the acceleration
Since the net external force is zero,
F = 0
Therefore
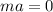
Acceleration can be rewritten as the derivative of velocity:
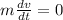
And using definition of momentum, p = mv,
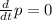
Which means that the total momentum does not change.