Answer:
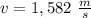
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that for circular motion the centripetal acceleration
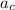 is:
is:
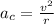
where v is the speed and r is the radius.
The centripetal acceleration for the astronaut must be the gravitational acceleration due to the gravity, as there are no other force. So
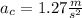 .
.
The radius of the orbit must be the radius of the Moon, plus the 270 km above the surface
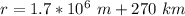
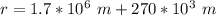
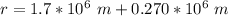
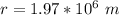
We can obtain the speed as:
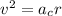
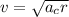

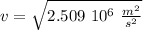
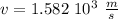
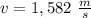
And this is the orbital speed.