Answer
The resistor has to be 100
Step-by-step explanation:
We will have to use the Current Divider Rule, that rule states:
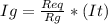
where:
Ig= Galvanometer current
It= Total current
Rg= Galvanometer Resistor
Req= Equivalent circuit resistor
For the case of two resistor in parallel:
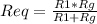
now:
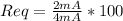
Req=50Ω
having the Equivalent resistor we can calculate R1 reformulating the Req formula:
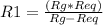
R1=100 Ω
So now when a 4mA current flows into the new circuit, 2mA will go through the Galvanometer deflecting the full scale.