Answer:
The difference of the ROE between financing with 30% debt and the ROE of financing only with common stocks is 0.07, in favor of financing with debt.
This difference is because it has an operational leverage: the return on assets is bigger than the interest paid for debt.
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to calculate the return on equity (ROE) for two situations:
1) No debt
In this case, all $3 millions of assets will be financed by common equity.
The EBT can be calculated as
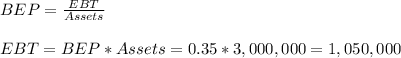
Then, if we take into account the tax rate, we calculate the earnings after tax:
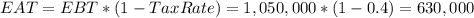
The ROE in this case is
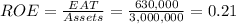
The return on equity (ROE) is 21% or $0.21 per $1 of equity.
2) With 30% debt
In this case, the assets are financed 30% by debt and 70% by common stocks.
The annual interest of this debt are
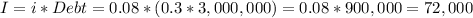
We can calculate now the EBT
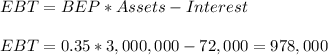
And the earning after tax
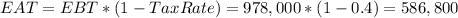
The ROE in this case is
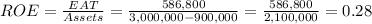
The return on equity (ROE) is 28% or $0.28 per $1 of equity.
The difference is because it has an operational leverage: the return on assets is bigger than the interest paid for debt.