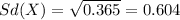Answer:
In order to check if we have a probability distirbution we need to satisfy some conditions:
1)
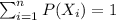
2)
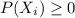
So then we satisfy the two conditions so then we have a probability distribution
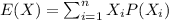
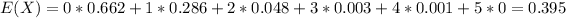
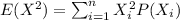
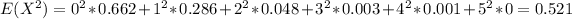
![Var(X)= E(X^2) -[E(X)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/mibopowx8u7kn4hgnlpapoe1pe8qq8zdl1.png)

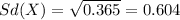
Explanation:
For this case we assume the following probability distribution:
X 0 1 2 3 4 5
P(X) 0.662 0.286 0.048 0.003 0.001 0.000
In statistics and probability analysis, the expected value "is calculated by multiplying each of the possible outcomes by the likelihood each outcome will occur and then summing all of those values".
The variance of a random variable Var(X) is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of X, E(X).
And the standard deviation of a random variable X is just the square root of the variance.
Solution to the problem
In order to check if we have a probability distirbution we need to satisfy some conditions:
1)
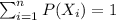
2)
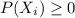
So then we satisfy the two conditions so then we have a probability distribution
For this case we can find the expected value with this formula:
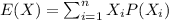
And replacing we got:
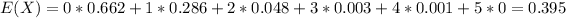
In order to calculate the variance we need to calculate the second moment with this formula:
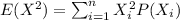
And replacing we got:
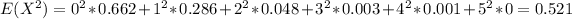
And the variance is given by:
![Var(X)= E(X^2) -[E(X)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/mibopowx8u7kn4hgnlpapoe1pe8qq8zdl1.png)
And replacing we got:

And the standard deviation would be: