Answer: The volume of oxygen gas needed is 156.8 L
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
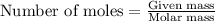
Given mass of methane = 56 g
Molar mass of methane = 16 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
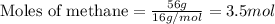
The chemical equation for the combustion of methane follows:
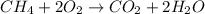
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of methane reacts with 2 moles of oxygen gas
So, 3.5 moles of methane will react with =
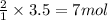 of oxygen gas
of oxygen gas
At STP:
1 mole of a gas occupies 22.4 L of volume
So, 7 moles of oxygen gas occupies
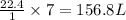 of volume
of volume
Hence, the volume of oxygen gas needed is 156.8 L