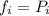Answer:
For thermodynamics the fugacity (fi) of a non ideal gas is defined as the product between the activity (ai) of the gas and 1 bar of pressure.
Step-by-step explanation:
For thermodynamics the fugacity (fi) of a non ideal gas is defined as the product between the activity (ai) of the gas and 1 bar of pressure.
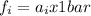
Also, in a gas mixture the fugacity (fi) of every component of the mixture is define by a coefficient of fugacity (Фi) multiplied by the partial pressure of the gas (Pi) :
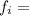 Ф
Ф
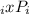
The coefficient of fugacity (Фi) is a measure of the deviation from the ideality of the gas. Thus, for an ideal gas Фi = 1 and the fugacity (fi) turns equal to partial pressure:
If Фi = 1 ⇒