Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Here, the assumption is that complete combustion of carbon is taking place. This means that there is no CO formation
Reaction equation when carbon is burning is as follows.
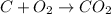
Molar mass of C = 12 kg/kmol
Molar mass of
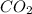 = 44 kg/kmol
= 44 kg/kmol
Hence, according to the stoichiometry,
1 Kmol of C reacted = 1 kmol of
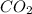 produced
produced
Therefore, 12 kg of C reacted = 44 kg
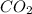 produced
produced
It is given that coal contains 50 mass % Carbon
So, 1 kg of coal contains (0.50 × 1)kg Carbon
Carbon in 1 kg Coal = 1 × 0.5 = 0.5 kg
As per the stoichiometry,
12 kg of C reacted = 44 kg
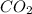 produced
produced
0.5 kg of C reacted = x kg
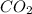 produced
produced
Therefore, value of x can be calculated as follows.
x =
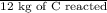
= 1.83 kg
This means that amount of
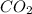 released is 1.83 kg.
released is 1.83 kg.
(b) It is assumed that coal contains 50 mass % carbon and 1 kg of coal burnt.
Since, it is given that energy density of coal is 24 Mj and efficiency of the power plant is 30%.
After burning 1 kg of coal amount of energy released = 24 Mj
Amount of energy converted to electricity =
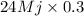 = 7.2 Mj
= 7.2 Mj
It is calculated that amount of
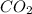 released per 1 kg of coal = 1.83 kg
released per 1 kg of coal = 1.83 kg
Therefore, calculate the amount of
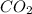 released in kg/Mj as follows.
released in kg/Mj as follows.
amount of
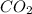 released in kg/Mj =
released in kg/Mj =
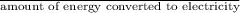
=
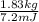
= 0.2541 kg/Mj
Hence, the production of
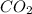 in kg/MJ is 0.2541 kg/Mj.
in kg/MJ is 0.2541 kg/Mj.