Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
 = 286 kJ =
= 286 kJ =
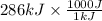
= 286000 J
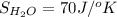 ,
,
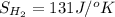
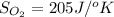
Hence, formula to calculate entropy change of the reaction is as follows.
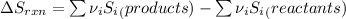
=
![[((1)/(2) * S_{O_(2)}) - (1 * S_{H_(2)})] - [1 * S_{H_(2)O}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/d1u0wtmemzgbicdpi2upcg74hyc41eoek2.png)
=
![[((1)/(2) * 205) + (1 * 131)] - [(1 * 70)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3u11qj83yjs15ahtvluhph6hvi2u4iw5i7.png)
= 163.5 J/K
Therefore, formula to calculate electric work energy required is as follows.
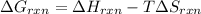
=
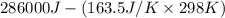
= 237.277 kJ
Thus, we can conclude that the electrical work required for given situation is 237.277 kJ.