Step-by-step explanation:
The heat transferred through conduction = heat transfer through radiation + heat transfer through convection
It is given that thermal conductivity of wall is 1 W/(m.K)
Boltzmann constant (
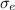 ) =
) =
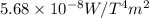
Formula to calculate the inner temperature of the furnace is as follows.
kA(T - 80) =
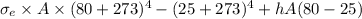
It is known that for black body emissitivity = 1
Now putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
kA(T - 80) =
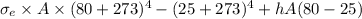
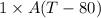 = A (
= A (
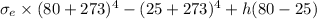 )
)
T - 80 =
![5.68 * 10^(-8) * [(353)^(4) - (298)^(4)] + 1 * 55](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ia9f41xhnjuwhpqr8yiw3ntnmaxj1a45rj.png)
T =
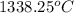
Thus, we can conclude that the inner temperature of the furnace wall is
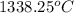 .
.