Answer:
(a) The amount of O2 needed is 2.67 pounds.
(b) The volume required is 847,509 litres.
(c) The heat given off as a result of the combustion to CO2 is 393.5 kJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
For a complete combustion of C to C02(g)
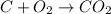
(a) The molecular mass of O2 is 32 g/mol and the molecular mass of C is 12 g/mol.
We need 1 mol O2 to burn 1 mol of C.
If we need 32 g of O2 to burn 12 g of C, to burn 1 pound of pure carbon charcoal we need (32/12)*1=2.67 pounds of O2.
(b) The density of O2, at atmospheric conditions, is 1.429 g/l. The volume of 2.67 pounds of O2 is
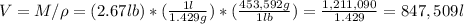
(c) To calculate the heat of the reaction, we have to look up in the Table of Standard Enthalpy of Formation Values and compute the following equation
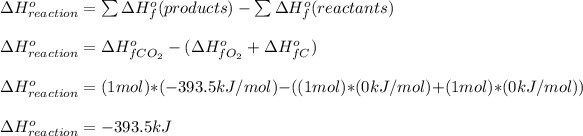
The heat given off as a result of the combustion to CO2 is 393.5 kJ.