Answer : The moles of
 left in the products are 0.16 moles.
left in the products are 0.16 moles.
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the moles of
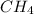 .
.
Using ideal gas equation:
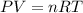
where,
P = pressure of gas = 1 atm
V = volume of gas = 10 L
T = temperature of gas =
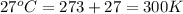
n = number of moles of gas = ?
R = gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol.K
Now put all the given values in the ideal gas equation, we get:
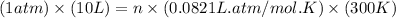
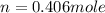
Now we have to calculate the moles of
 .
.
The balanced chemical reaction will be:
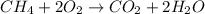
From the balanced reaction we conclude that,
As, 1 mole of
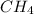 react with 2 moles of
react with 2 moles of

So, 0.406 mole of
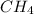 react with
react with
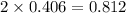 moles of
moles of

Now we have to calculate the excess moles of
 .
.
 is 20 % excess. That means,
is 20 % excess. That means,
Excess moles of
 =
=
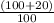 × Required moles of
× Required moles of

Excess moles of
 = 1.2 × Required moles of
= 1.2 × Required moles of

Excess moles of
 = 1.2 × 0.812 = 0.97 mole
= 1.2 × 0.812 = 0.97 mole
Now we have to calculate the moles of
 left in the products.
left in the products.
Moles of
 left in the products = Excess moles of
left in the products = Excess moles of
 - Required moles of
- Required moles of

Moles of
 left in the products = 0.97 - 0.812 = 0.16 mole
left in the products = 0.97 - 0.812 = 0.16 mole
Therefore, the moles of
 left in the products are 0.16 moles.
left in the products are 0.16 moles.