Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Initial volume (
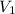 ) = 100
) = 100
Final volume (
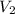 ) = 10
) = 10
Initial pressure (
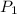 ) = 50 psia = 50
) = 50 psia = 50
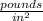
Temperature =
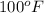
So, we assume that vapors are also ideal gas.
Hence, the work done for ideal gas will be calculated as follows.
W =
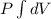
Since, it is given that the temperature is constant so, it is an isothermal process.
Therefore, work done for isothermal process is as follows.
W =
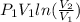
Putting the values into the above formula as follows.
W =
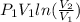
=
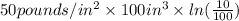
= -11512.925 lbf-in
As there are 12 inch present in 1 ft. So, converting lbf-in into lbf-ft as follows.
W =
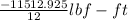
= -959.41 lbf-ft
The negative sign means work is supplied.
Thus, we can conclude that the work done is -959.41 lbf-ft.