Answer : The correct option is, (b) 20 kPa
Explanation :
The Raoult's law for liquid phase is:
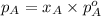 .............(1)
.............(1)
where,
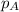 = partial vapor pressure of A
= partial vapor pressure of A
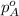 = vapor pressure of pure substance A
= vapor pressure of pure substance A
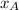 = mole fraction of A
= mole fraction of A
The Raoult's law for vapor phase is:
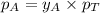 .............(2)
.............(2)
where,
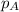 = partial vapor pressure of A
= partial vapor pressure of A
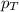 = total pressure of the mixture
= total pressure of the mixture
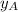 = mole fraction of A
= mole fraction of A
Now comparing equation 1 and 2, we get:
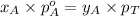
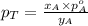 ............(3)
............(3)
First we have to calculate the total pressure of the mixture.
Given:
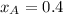 and
and
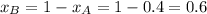
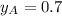 and
and
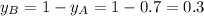
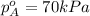
Now put all the given values in equation 3, we get:
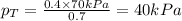
Now we have to calculate the vapor pressure of B.
Formula used :
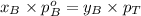
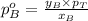
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get:
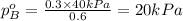
Therefore, the vapor pressure of B is 20 kPa.