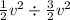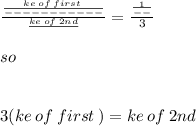Answer:
The object with a higher mass has three times the kinetic energy of the less massive object.
We know that K.E.= 1/2 mv²
mass of first object = 1kg
speed = v
So K.E. = 1/2mv²
= 1/2 × (1) × v²
=
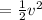
Now the mass of second body = 3kg
speed = v
So K.E. = 1(3)v²/2
=
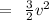
now
K.E of first / KE of 2nd