Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction equation is as follows.
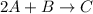
So, rate constants for different reactants and products written as follows.
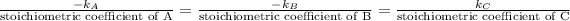
As per the reaction equation, the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products are as follows.
A = -2
B = -1
C = 1
Therefore,
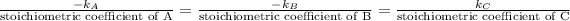
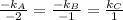
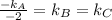
Hence,
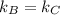 =
=
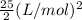
= 12.5
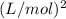
Thus, we can conclude that
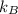 and
and
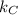 are 12.5
are 12.5
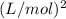 .
.