Step-by-step explanation:
We have three genes in the same chromosome and are trying to determine their order and relative distance to each other.
The genes and possible alleles are:
- claret (c/c+)
- spineless (s/s+)
- hairless (h/h+)
All mutations are recessive: two copies of the mutant allele are needed for the fly to show that trait.
Parental cross
- claret hairless male:
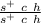
- spineless female:
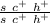
Each parent can produce 1 type of gamete only, so the F1 will be homogeneous:
F1
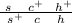
During meiosis, the F1 females can produce 8 types of gametes: 2 parentals and 6 recombinants (two of them, the result of a double crossing over).
If they are test crossed to homozygous recessive males (which can only produce a
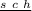 gamete), the following phenotypes are obtained (I just write the alleles they inherited from the female fly, as the ones that came from the male are the same for all of them):
gamete), the following phenotypes are obtained (I just write the alleles they inherited from the female fly, as the ones that came from the male are the same for all of them):
- 321 spineless (s c+ h+) ----> Parental
- 309 claret, hairless (s+ c h) ----> Parental
- 130 claret, spineless (s c h+) ----> Recombinant
- 140 hairless (s+ c+ h) ----> Recombinant
- 32 hairless, claret, spineless (s c h) ----> Recombinant
- 38 WT (s+ c+ h+) ----> Recombinant
- 18 claret (s+ c h+) ----> Double Recombinant
- 12 hairless, spineless (s c+ h) ----> Double Recombinant
The phenotypes observed in the highest frequency are always the parentals, and the ones in the lowest frequency are always the double recombinants.
To determine the order of the genes:
- we have to write down the genotype of the F1 female three times, changing the order of the genes each time.
- Then, we hypothesize what the double recombinant gametes would look like.
- When the theoretical double recombinants we obtain are the same as the ones observed in the F2, we know that that is the correct order of the genes.
In this problem, only if the middle gene is h+/h the double crossing over gives us the observed double recombinant gametes, therefore hairless is the middle gene.
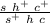
Double recombinants:
- s h c+ ----> spineless hairless
- s+ h+ c ----> claret
To determine the distance between the genes:
Genetic distance (m.u.) = Recombination Frequency x 100
- Distance between the spineless and hairless genes:
![Distance \ [s-h]= (number\ of\ recombinants \ [s-h])/(Total number of individuals) * 100\\\\\\Distance \ [s-h]= (32+38+12+18)/(1000) * 100\\\\Distance \ [s-h]= 10\ map\ units](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/high-school/440sc8jte0ho8irrvr5dllfgg19key3240.png)
- Distance between the hairless and claret genes:
![Distance \ [h-c]= (130+140+12+18)/(1000) * 100\\\\Distance \ [h-c]= 30\ map\ units](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/high-school/toim92pn2but9f7o5qgaecwb0ec6if9f6d.png)
The gene map for these genes is:
spineless -----------------hairless ---------------------------claret
10 m.u. 30 m.u.