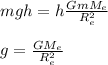Answer:
g = G mE /Re^2
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
First of all we need to find an equation where we can apply the series expansion of (1+x)^-1 where the variable x be a small number.
Since we are considering that h<<Re this implies that (h/Re)<<1 so this is the small number we are looking for.
Then in the equation for the earth's potential we can take of the earths radius as:
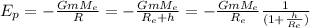
Now we can define x=h/Re and use the series expansion. Therefore:
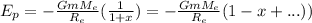
Since x is a small number, x^2 will be even smaller, tehrefore we will only consider the first power of x:
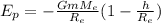
and: