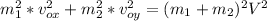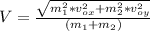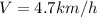Answer:
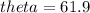 °
°
θ is the angle that goes from the positive x axis to the positive y axis
Step-by-step explanation:
The skaters collide in a completely inelastic collision, in other words they have the same velocity after the collision, this velocity has a magnitude V and an angle respect the axis X.
We need to use the conservation of momentum Law, the total momentum is the same before and after the collision.
In the axis X:
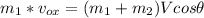 (1)
(1)
In the axis Y:
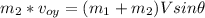 (2)
(2)
We solve the last equations, we divide them:
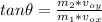
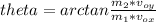
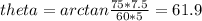 °
°
θ is the angle that goes from the positive x axis to the positive y axis
We add the squares of the equations (1) and (2):