Answer and Explanation:
The overall energy of a very bright source of red light is more than that of the dim blue light source.
The reason for this is because red light has the longest wavelength and contains larger number of photons as compared to the blue light.
But if the energy associated with a particular photon is to be considered than the energy of any individual photon is lower than the energy of any photon of blue light due to the lower frequency of the lower frequency of the red light.
To understand this, we consider the eqn:
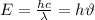
where
E = Energy of the photon
h = Planck constant
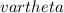 = frequency
= frequency
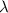 = wavelength
= wavelength
Thus the above relation shows that energy is inversely related to wavelength and directly related to frequency.
Thus the energy of the individual photon of red light is not sufficient to eject an electron from the photosensitive surface with the required amount oft energy.
Since, to eject an electron from the surface, it is essential to have a photon of the corresponding required energy to incident and get absorbed thus ejecting an electron with the corresponding energy.
Thus irrespective of the number of photons present in the bright red light source, it will have no effect on the photosensitive surface's electrons.