Answer:
A) 2.69 M
B) 0.059
Step-by-step explanation:
A) We have:
33.8% solute by mass= 33.8 g solute/100 g solution
molarity = mol solute/ 1 L solution
molarity=
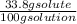 x
x
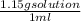 x
x
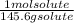 x
x
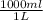
molarity= 2.69 mol solute/L solution = 2.69 M
B) We know that there are 33.8 g of solute in 100 g of solution.
As the total solution is compounded by solute+solvent (in this case, solvent is water), the mass of water is the difference between the mass of the total solution and the mass of solute:
mass of water= 100 g - 33.8 g = 66.2 g
Now, we calculate the number of mol of both solute and water:
mol solute= 33.8 g solute x
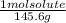 = 0.232 mol
= 0.232 mol
mol H20= 66.2 g H₂O x
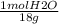
Finally, the mol fraction of solute (Xsolute) is calculated as follows:
Xsolute=
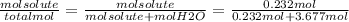
Xsolute= 0.059