Answer: The pH of resulting solution is 9.08
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
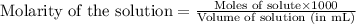 ........(1)
........(1)
Molarity of HCl = 0.40 M
Volume of solution = 15.0 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
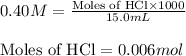
Molarity of ammonia = 0.50 M
Volume of solution = 20.0 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
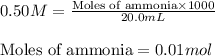
The chemical reaction for hydrochloric acid and ammonia follows the equation:
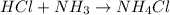
Initial: 0.006 0.01
Final: - 0.004 0.006
Volume of solution = 15.0 + 20.0 = 35.0 mL = 0.035 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
- To calculate the pOH of basic buffer, we use the equation given by Henderson Hasselbalch:
![pOH=pK_b+\log(([salt])/([base]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/sczgwwurez8svwaa6wk2y4tedmhd42roec.png)
![pOH=pK_b+\log(([NH_4Cl])/([NH_3]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cw3c47w8uvge8pcio9rigo5b0fyt28m2bo.png)
We are given:
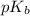 = negative logarithm of base dissociation constant of ammonia =
= negative logarithm of base dissociation constant of ammonia =
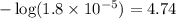
![[NH_4Cl]=(0.006)/(0.035)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/u13suumvrjdqrdmn119ztvry3dr0hph7xf.png)
![[NH_3]=(0.004)/(0.035)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7tp9ajfburzkiho8orfkxc4syghl9sf5le.png)
pOH = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
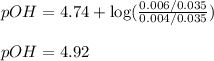
To calculate pH of the solution, we use the equation:
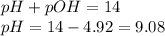
Hence, the pH of the solution is 9.08