Answer:
a.
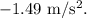
b.
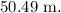
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
- Velocity of the particle, v(t) = 3 cos(mt) = 3 cos (0.5t) .
(a):
The acceleration of the particle at a time is defined as the rate of change of velocity of the particle at that time.
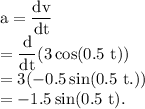
At time t = 3 seconds,
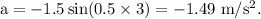
Note: The arguments of the sine is calculated in unit of radian and not in degree.
(b):
The velocity of the particle at some is defined as the rate of change of the position of the particle.
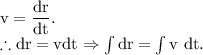
For the time interval of 2 seconds,
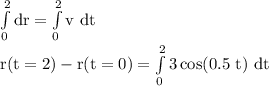
The term of the left is the displacement of the particle in time interval of 2 seconds, therefore,
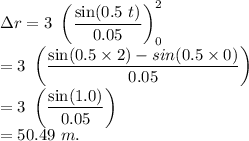
It is the displacement of the particle in 2 seconds.