Answer:
See solution below
Explanation:
(a) If n=0 or 1, the equation
(1)
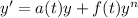
would be a simple linear differential equation. So, we can assume that n is different to 0 or 1.
Let's use the following substitution:
(2)
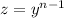
Taking the derivative implicitly and using the chain rule:
(3)
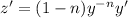
Multiplying equation (1) on both sides by
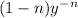
we obtain the equation
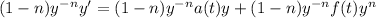
reordering:
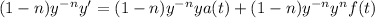
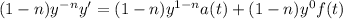
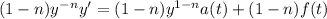
Now, using (2) and (3) we get:
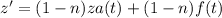
which is an ordinary linear differential equation with unknown function z(t).
(b)
The equation we want to solve is
(4)
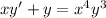
Here, our independent variable is x (instead of t)
Assuming x different to 0, we divide both sides by x to obtain:
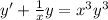
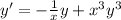
Which is an equation of the form (1) with
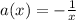
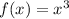
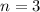
So, if we substitute
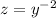
we transform equation (4) in the lineal equation
(5)
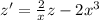
and this is an ordinary lineal differential equation of first order whose
integrating factor is
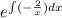
but
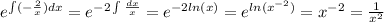
Similarly,
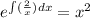
and the general solution of (5) is then
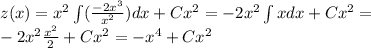
where C is any real constant
Reversing the substitution
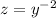
we obtain the general solution of (4)
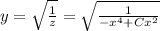
Attached there is a sketch of several particular solutions corresponding to C=1,4,6
It is worth noticing that the solutions are not defined on x=0 and for C<0