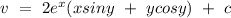Answer:

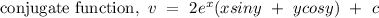
Explanation:
As given in question,
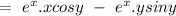
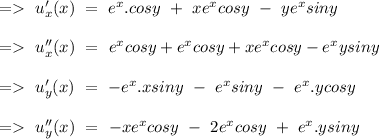
For a system to be harmonic,
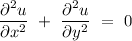
From the above calculated value we can see that
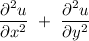
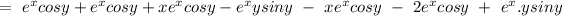
= 0
So, given function u(x) is harmonic.
Now to find conjugate function of u,
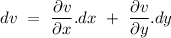
According to Cauchy-Riemen Equation,
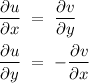
So, we4 can write the above equation as,
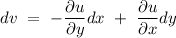
on putting the values, we have
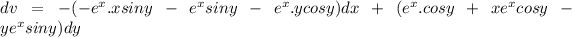
on integrating both side, we get
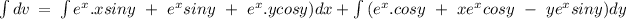
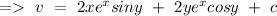
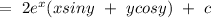
hence, the conjugate equation can be given by