Answer:
The matrix form of the system of equations is
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&1&1&1&-3\\1&-1&-2&1&2\\2&0&1&-1&1\end{array}\right] \left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&w&z&u\end{array}\right] =\left[\begin{array}{c}5&4&3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ib7m7obdup25an2fh0bh5l5kuy6fa7sf80.png)
The reduced row echelon form is
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&1/4&0&3\\0&1&0&9/4&-4&5\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/x0kbksy7do275fvwcr5ughln7gqwrtwun6.png)
The vector form of the general solution for this system is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&w&z&u\end{array}\right]=u\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&(5)/(2)&0&(2)/(3)&1\end{array}\right]+w\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&-(3)/(2)&1&(2)/(3)&0\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}(5)/(2)&(1)/(2)&0&2&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/hmwzdm0t2cddtne7e9un16tj960ibfshi6.png)
Explanation:
- Convert the given system of equations to matrix form
We have the following system of linear equations:
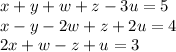
To arrange this system in matrix form (Ax = b), we need the coefficient matrix (A), the variable matrix (x), and the constant matrix (b).
so
![A= \left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&1&1&1&-3\\1&-1&-2&1&2\\2&0&1&-1&1\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/mz8a9985ckzhdfez1whyt8myxjxzi6xkz2.png)
![x=\left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&w&z&u\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/kynzrexeh5q83gu320omake1l67mnek04s.png)
![b=\left[\begin{array}{c}5&4&3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ugch1m2gm1ursz2o6u6a3hyq9ehjrjlfgt.png)
- Use row operations to put the augmented matrix in echelon form.
An augmented matrix for a system of equations is the matrix obtained by appending the columns of b to the right of those of A.
So for our system the augmented matrix is:
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&1&1&-3&5\\1&-1&-2&1&2&4\\2&0&1&-1&1&3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/dhgn26nsno7vd7mum1hi8itx3805fq7eqh.png)
To transform the augmented matrix to reduced row echelon form we need to follow this row operations:
- add -1 times the 1st row to the 2nd row
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&-2&-3&0&5&-1\\2&0&1&-1&1&3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/xowiy1fgjeiyjqgfxhnwjaz6zhnsqjngwr.png)
- add -2 times the 1st row to the 3rd row
![\left[\begin{array}c1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&-2&-3&0&5&-1\\0&-2&-1&-3&7&-7\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/cm7swrphihenucilr3k3oi5ixuspoekt39.png)
- multiply the 2nd row by -1/2
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&1&3/2&0&-5/2&1/2\\0&-2&-1&-3&7&-7\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/frpqqe7dmucf2w6vjfjw6eke4fw8wi2sg6.png)
- add 2 times the 2nd row to the 3rd row
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&1&3/2&0&-5/2&1/2\\0&0&2&-3&2&-6\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/fzzsveqnwc5aiwn8rftnl4eborlebhdshj.png)
- multiply the 3rd row by 1/2
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&1&3/2&0&-5/2&1/2\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/2jmm8fvn4fqdlpik35jtg1tv7v36y38wux.png)
- add -3/2 times the 3rd row to the 2nd row
![\left[\begin{array}c1&1&1&1&-3&5\\0&1&0&9/4&-4&5\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/3alozy5vvalwsb7znn3cgcw3ndcxs3hjms.png)
- add -1 times the 3rd row to the 1st row
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&1&0&5/2&-4&8\\0&1&0&9/4&-4&5\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/exdp4z3ad9h5pquv149wt1jfbxcdda6r8t.png)
- add -1 times the 2nd row to the 1st row
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&0&0&1/4&0&3\\0&1&0&9/4&-4&5\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/x0kbksy7do275fvwcr5ughln7gqwrtwun6.png)
- Find the solutions set and put in vector form.
Interpret the reduced row echelon form:
The reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix is
![\left[\begin{array}ccccc1&0&0&1/4&0&3\\0&1&0&9/4&-4&5\\0&0&1&-3/2&1&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/x0kbksy7do275fvwcr5ughln7gqwrtwun6.png)
which corresponds to the system:
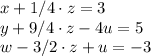
We can solve for z:
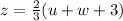
and replace this value into the other two equations
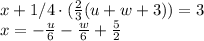
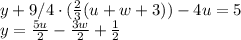
No equation of this system has a form zero = nonzero; Therefore, the system is consistent. The system has infinitely many solutions:
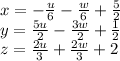
where u and w are free variables.
We put all 5 variables into a column vector, in order, x,y,w,z,u
![x=\left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&w&z&u\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c}-(u)/(6) -(w)/(6)+(5)/(2)&(5u)/(2)-(3w)/(2)+(1)/(2)&w&(2u)/(3)+(2w)/(3)+2&u\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/relfj0m7aluo0fti935n19sm75wf8p44yr.png)
Next we break it up into 3 vectors, the one with all u's, the one with all w's and the one with all constants:
![\left[\begin{array}{c}-(u)/(6)&(5u)/(2)&0&(2u)/(3)&u\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}-(w)/(6)&-(3w)/(2)&w&(2w)/(3)&0\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}(5)/(2)&(1)/(2)&0&2&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/gvoq2wlvznnsuz0v3i5q683b3zz5cj99m4.png)
Next we factor u out of the first vector and w out of the second:
![u\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&(5)/(2)&0&(2)/(3)&1\end{array}\right]+w\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&-(3)/(2)&1&(2)/(3)&0\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}(5)/(2)&(1)/(2)&0&2&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/dqau7l5szgmgmvgbkfloqeh9hloxmkyc4d.png)
The vector form of the general solution is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&w&z&u\end{array}\right]=u\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&(5)/(2)&0&(2)/(3)&1\end{array}\right]+w\left[\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(6)&-(3)/(2)&1&(2)/(3)&0\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}(5)/(2)&(1)/(2)&0&2&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/hmwzdm0t2cddtne7e9un16tj960ibfshi6.png)