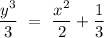Answer:
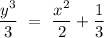
Explanation:
According to the given question,
The given differential equation is
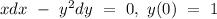
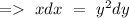
On integrating both sides, we will have
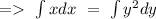
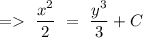 (1)
(1)
Now, according to question
y(0)=1
so, we can write
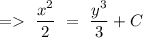
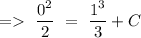
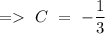
Now, by putting the value of C in equation (1), we will get
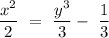
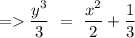
So, the solution of given differential equation will be