Answer:
The equilibrium concentration of CH₃OH is 0.28 M
Step-by-step explanation:
For the reaction: CO (g) + 2H₂(g) ↔ CH₃OH(g)
The equilibrium constant (Keq) is given for the following expresion:
Keq=
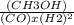 =14.5
=14.5
Where (CH3OH), (CO) and (H2) are the molar concentrations of each product or reactant.
We have:
(CH3OH)= ?
(CO)= 0.15 M
(H2)= 0.36 M
So, we only have to replace the concentrations in the equilibrium constant expression to obtain the missing concentration we need:
14.5=
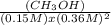
14.5 x (0.15 M) x
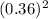 = (CH₃OH)
= (CH₃OH)
0.2818 M = (CH₃OH)