Answer:
(a)
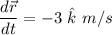
(b) Instantaneous velocity of the object is represented by
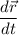 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
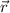 = the position vector of the object at any time instant =
= the position vector of the object at any time instant =
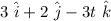
where
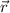 is in meters and
is in meters and
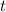 is in seconds.
is in seconds.
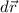 = small change in position vector
= small change in position vector
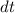 = small change in time
= small change in time
Part (a):
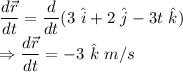
Part (b):
As we know that the rate of change of position is the velocity of a particle which is calculated by the differential of the position vector of the particle at with respect to time. This differential gives us a unit vector along negative z-axis having unit as m/s. So, the physical quantity represented by
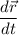 is the instantaneous velocity of the object.
is the instantaneous velocity of the object.