Answer:
PNO₂ = 0.49 atm
PN₂O₄ = 0.45 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's begin with the equation of ideal gas, and derivate from it an equation that involves the density (ρ = m/V).
PV = nRT
n = m/M (m is the mass, and M the molar mass)
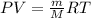
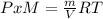
PxM = ρRT
ρ = PxM/RT
With the density of the gas mixture, we can calculate the average of molar mass (Mavg), with the constant of the gases R = 0.082 atm.L/mol.K, and T = 16 + 273 = 289 K
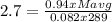
0.94Mavg = 63.9846
Mavg = 68.0687 g/mol
The molar mass of N is 14 g/mol and of O is 16 g/mol, than
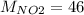 g/mol and
g/mol and
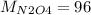 g/mol. Calling y the molar fraction:
g/mol. Calling y the molar fraction:
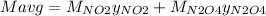
And,
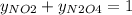
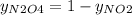
So,
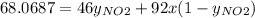
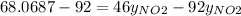
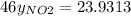
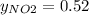
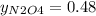
The partial pressure is the molar fraction multiplied by the total pressure so:
PNO₂ = 0.52x0.94 = 0.49 atm
PN₂O₄ = 0.48x0.94 = 0.45 atm