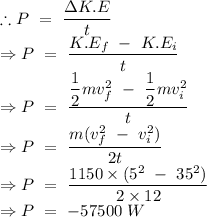Answer:
part (a) 46958.33 W
part (b) 43125 W
part (c) -57500 W
Step-by-step explanation:
Given,
- Mass of the car = m = 1150 kg
- Angle of inclination of the hill =
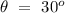
- Total time taken = t = 12 s
part (a)
Given that the velocity is constant,
Total displacement traveled by the car = s = 100 m
Work done by the car to reach at the top of the hill
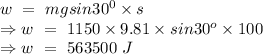
Hence, power
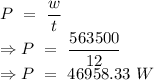
part (b)
Given,
- final velocity =
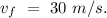
- Initial velocity =
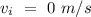
Total power is equal to the ratio of the change in kinetic energy and total time taken
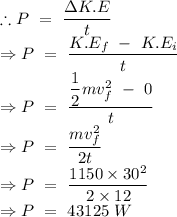
part (c)
- Initial velocity of the car =
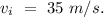
- Final velocity of the car =
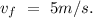
Total power is equal to the ratio of the change in kinetic energy and total time taken