Answer:
a) kc = 0,25
b) [A] = 0,41 M
c) [A] = 0,8 M
[B] =0,2 M
[C] = 0,2M
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium-constant expression is defined as the ratio of the concentration of products over concentration of reactants. Each concentration is raised to the power of their coefficient.
Also, pure solid and liquids are not included in the equilibrium-constant expression because they don't affect the concentration of chemicals in the equilibrium.
If global reaction is:
A(g) + B(g) ⇋ 2 C(g) + D(s)
The kc =
![([C]^2)/([A][B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tdvbuqi7mjusknzisytzyvoz8m7rboils8.png)
a) The concentrations of each compound are:
[A] =
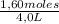 = 0,4 M
= 0,4 M
[B] =
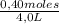 = 0,1 M
= 0,1 M
[C] =
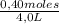 = 0,1 M
= 0,1 M
kc =
![([0,1]^2)/([0,4][0,1])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8128mxc7hdnzcx8v3kmlijqct1820ri2qg.png) = 0,25
= 0,25
b) The addition of B and D in the same amount will, in equilibrium, produce these changes:
[A] =
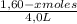
[B] =
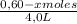
[C] =
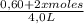
0,25 =
![([0,60+2x]^2)/([1,60-x][0,60-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4ew0g8ugfhuw1yn1tk09npzaxrmkbpa8c2.png)
You will obtain
3,75x² +2,95x +0,12 = 0
Solving
x =-0,74363479081119 → No physical sense
x =-0,043031875855476
Thus, concentration of A is:
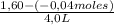 = 0,41 M
= 0,41 M
c) When volume is suddenly halved concentrations will be the concentrations in equilibrium over 2L:
[A] =
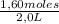 = 0,8 M
= 0,8 M
[B] =
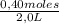 = 0,2 M
= 0,2 M
[C] =
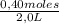 = 0,2M
= 0,2M
I hope it helps!