Answer:
For ball P=- 2 x m x V.
For P= - m x V
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that
if external force is zero then linear momentum of system will be conserve.
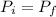
Rubber ball:
Given that speed of ball is V before the collision with ball.
The speed of the ball is remain after the collision with ball but the direction will reverse.
Lets take first ball is moving in positive x direction and after collision with ball it moves in negative x direction.
Initial momentum
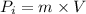
Finall momentum
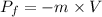
So the change in the momentum
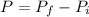
P=- 2 x m x V.
For clay:
Initial velocity of clay is V in positive x direction and final velocity is zero because it stick with the wall
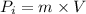
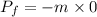
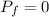
So the change in the momentum
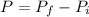
P= - m x V.