Answer:
The wire now has less (the half resistance) than before.
Step-by-step explanation:
The resistance in a wire is calculated as:
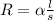
Were:
R is resistance
 is the resistance coefficient
is the resistance coefficient
l is the length of the material
s is the area of the transversal wire, in the case of wire will be circular area (
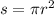 ).
).
So if the lenght and radius are doubled, the equation goes as follows:
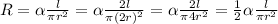
So finally because the circular area is a square function, the resulting equation is half of the one before.