Answer:
1. 170,9 g of AlCl₃ and 142,5 g of Ca(OH)₂
2. 108,0 g of HgO
3. 112,0 g of Ba(NO₃)₂ and 68,39 g of CuSO₄
4. 60,32 g of PbCl₂ and 72,01 g of KI
5. 81,63 g of Na₂S and 140,6 g of CuCl₂
Step-by-step explanation:
1. The reaction is:
2 AlCl₃ + 3 Ca(OH)₂ → 2 Al(OH)₃ + 3 CaCl₂
The insoluble product is Al(OH)₃. To produce 100,0 g you need to add:
100,0 g ×
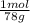 = 1,282 moles of Al(OH)₃.
= 1,282 moles of Al(OH)₃.
Thus, the grams of AlCl₃ and Ca(OH)₂ you need are:
1,282 moles of Al(OH)₃ ×
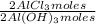 = 1,282 moles of AlCl₃ ×
= 1,282 moles of AlCl₃ ×
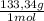 = 170,9 g of AlCl₃
= 170,9 g of AlCl₃
1,282 moles of Al(OH)₃ ×
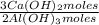 = 1,923 moles of Ca(OH)₂ ×
= 1,923 moles of Ca(OH)₂ ×
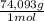 = 142,5 g of Ca(OH)₂
= 142,5 g of Ca(OH)₂
2. The reaction is:
2 HgO + → 2 Hg + O₂
The insoluble product is Hg. To produce 100,0 g you need to add:
100,0 g ×
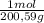 = 0,4985 moles of Hg.
= 0,4985 moles of Hg.
Thus, the grams of HgO you need are:
0,4985 moles of Hg ×
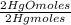 = 0,4985 moles of HgO ×
= 0,4985 moles of HgO ×
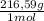 = 108,0 g of HgO
= 108,0 g of HgO
3. The reaction is:
Ba(NO₃)₂ + CuSO₄ → BaSO₄ + Cu(NO₃)₂
The insoluble product is BaSO₄. To produce 100,0 g you need to add:
100,0 g ×
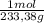 = 0,4285 moles of BaSO₄.
= 0,4285 moles of BaSO₄.
Thus, the grams of Ba(NO₃)₂ and CuSO₄ you need are:
0,4285 moles of BaSO₄ ×
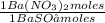 = 0,4285 moles of Ba(NO₃)₂ ×
= 0,4285 moles of Ba(NO₃)₂ ×
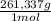 = 112,0 g of Ba(NO₃)₂
= 112,0 g of Ba(NO₃)₂
0,4285 moles of BaSO₄ ×
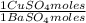 = 0,4285 moles of CuSO₄ ×
= 0,4285 moles of CuSO₄ ×
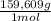 = 68,39 g of CuSO₄
= 68,39 g of CuSO₄
4. The reaction is:
PbCl₂ + 2 KI → PbI₂ + 2 KCl
The insoluble product is PbI₂. To produce 100,0 g you need to add:
100,0 g ×
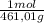 = 0,2169 moles of PbI₂.
= 0,2169 moles of PbI₂.
Thus, the grams of PbCl₂ and KI you need are:
0,2169 moles of PbI₂ ×
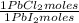 = 0,2169 moles of PbCl₂ ×
= 0,2169 moles of PbCl₂ ×
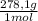 = 60,32 g of PbCl₂
= 60,32 g of PbCl₂
0,2169 moles of PbI₂ ×
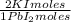 = 0,4338 moles of KI ×
= 0,4338 moles of KI ×
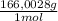 = 72,01 g of KI
= 72,01 g of KI
5. The reaction is:
Na₂S + CuCl₂ → CuS + 2 NaCl
The insoluble product is CuS. To produce 100,0 g you need to add:
100,0 g ×
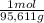 = 1,046 moles of CuS.
= 1,046 moles of CuS.
Thus, the grams of Na₂S and CuCl₂ you need are:
1,046 moles of CuS ×
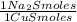 = 1,046 moles of Na₂S ×
= 1,046 moles of Na₂S ×
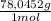 = 81,63 g of Na₂S
= 81,63 g of Na₂S
1,046 moles of CuS ×
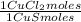 = 1,046 moles of CuCl₂ ×
= 1,046 moles of CuCl₂ ×
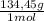 = 140,6 g of CuCl₂
= 140,6 g of CuCl₂
I hope it helps!